Django Custom Admin
A custom admin interface on Vue 3 and Vuetify with DRF backend that tries to Keep It Simple.
Features
- Interface for DRF API based on Vue 3 and Vuetify
- Pre-builded Vue SPA front page provided through Django template/static files. A separate setup for the front end is not required.
- Ability to create inline admin actions using forms via DRF serializers
- Dynamic system for obtaining partition scheme and interface structure
- Access rights sharing system based on DRF permissioins
Custom fields
- Related fields/filters with autocomplete search
- WYSIWYG editor using TinyMCE
- JSON editor using svelte-jsoneditor and JSONForms
- Autocomplete for related fields and filters using API
- Support for django-modeltranslation translations
Non ORM inlines
- Table views
- Support for graphs using chartjs
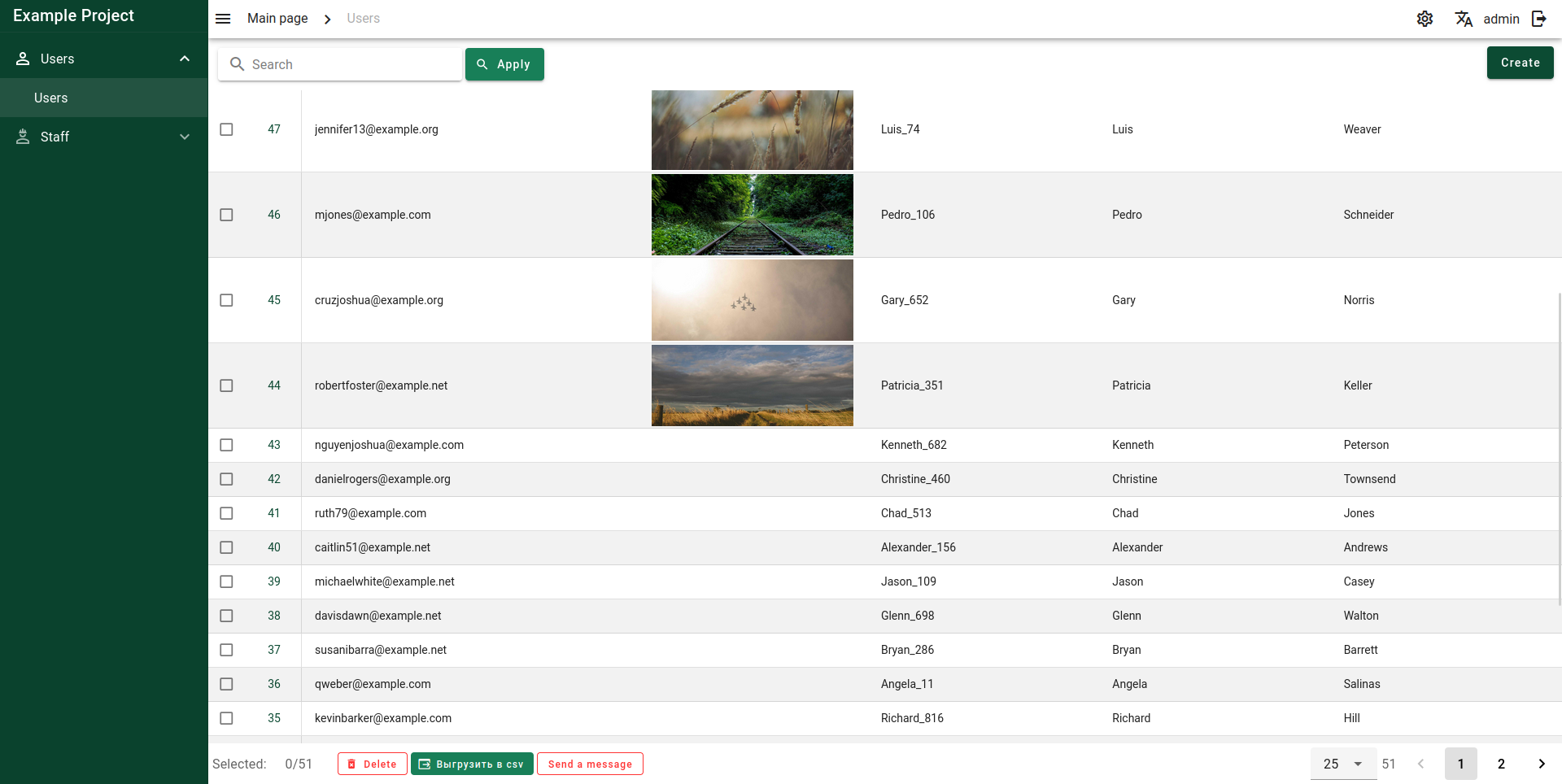
Screenshots
Login page
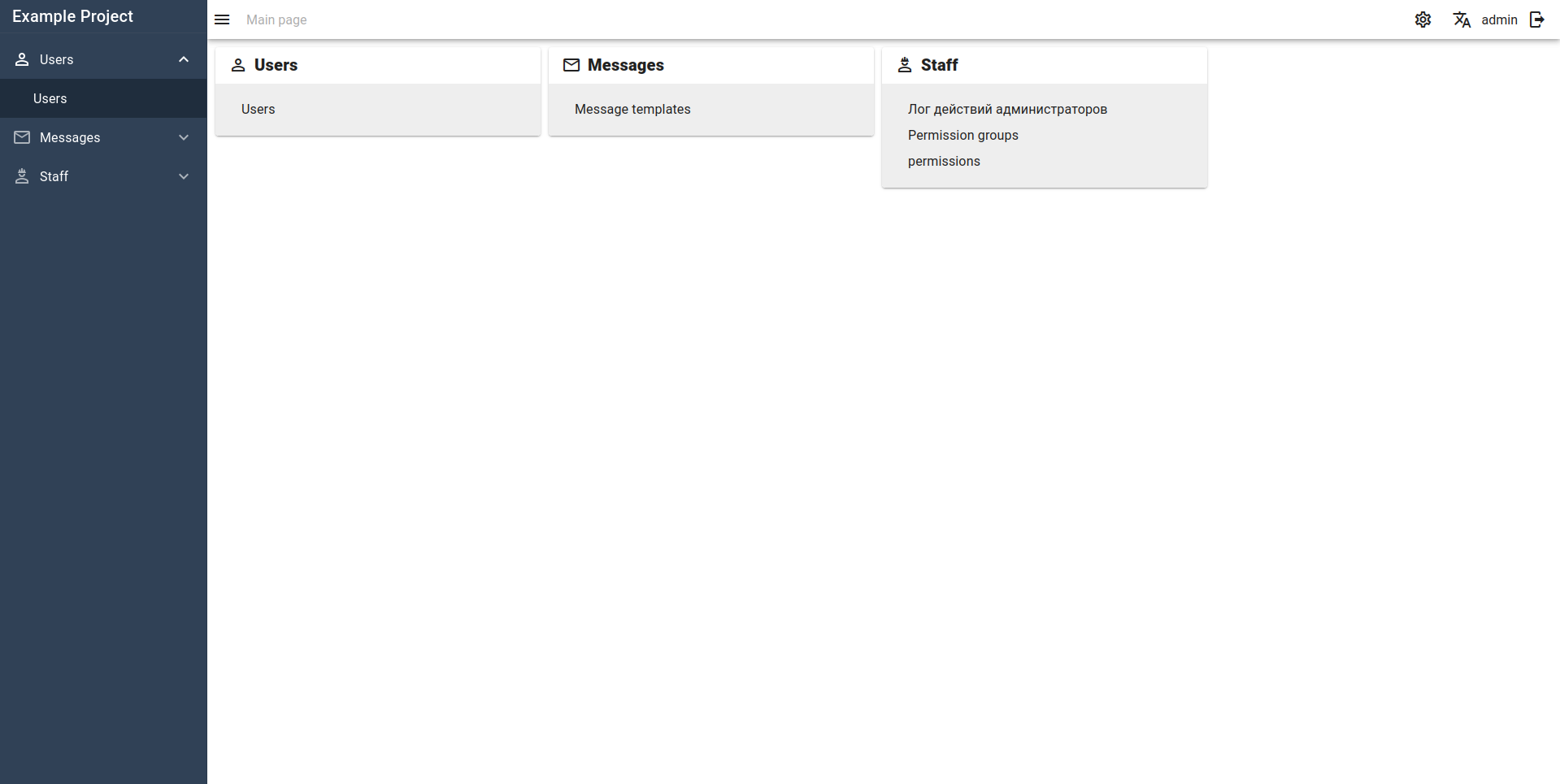
Dashboard
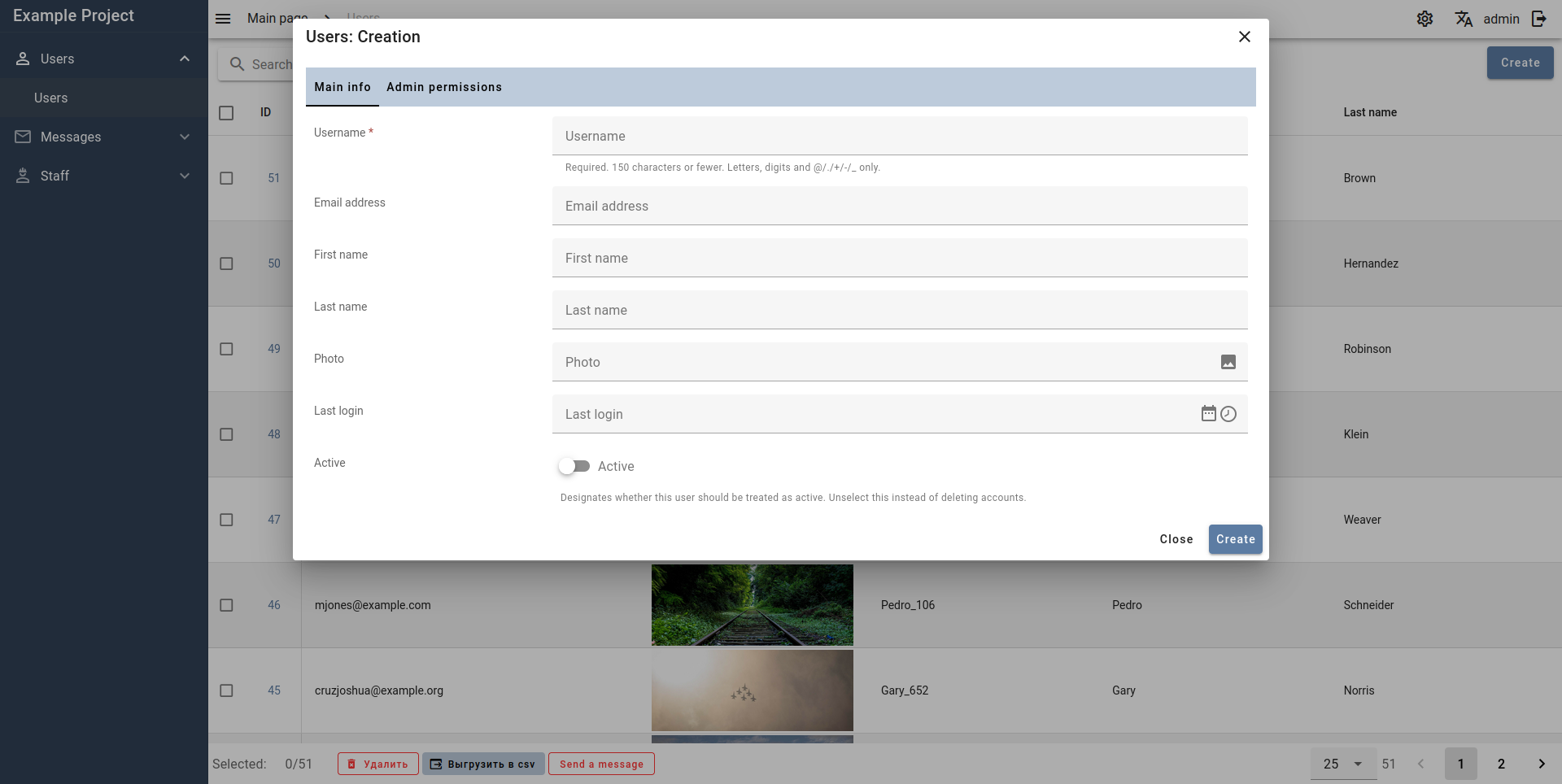
Create view
Edit page
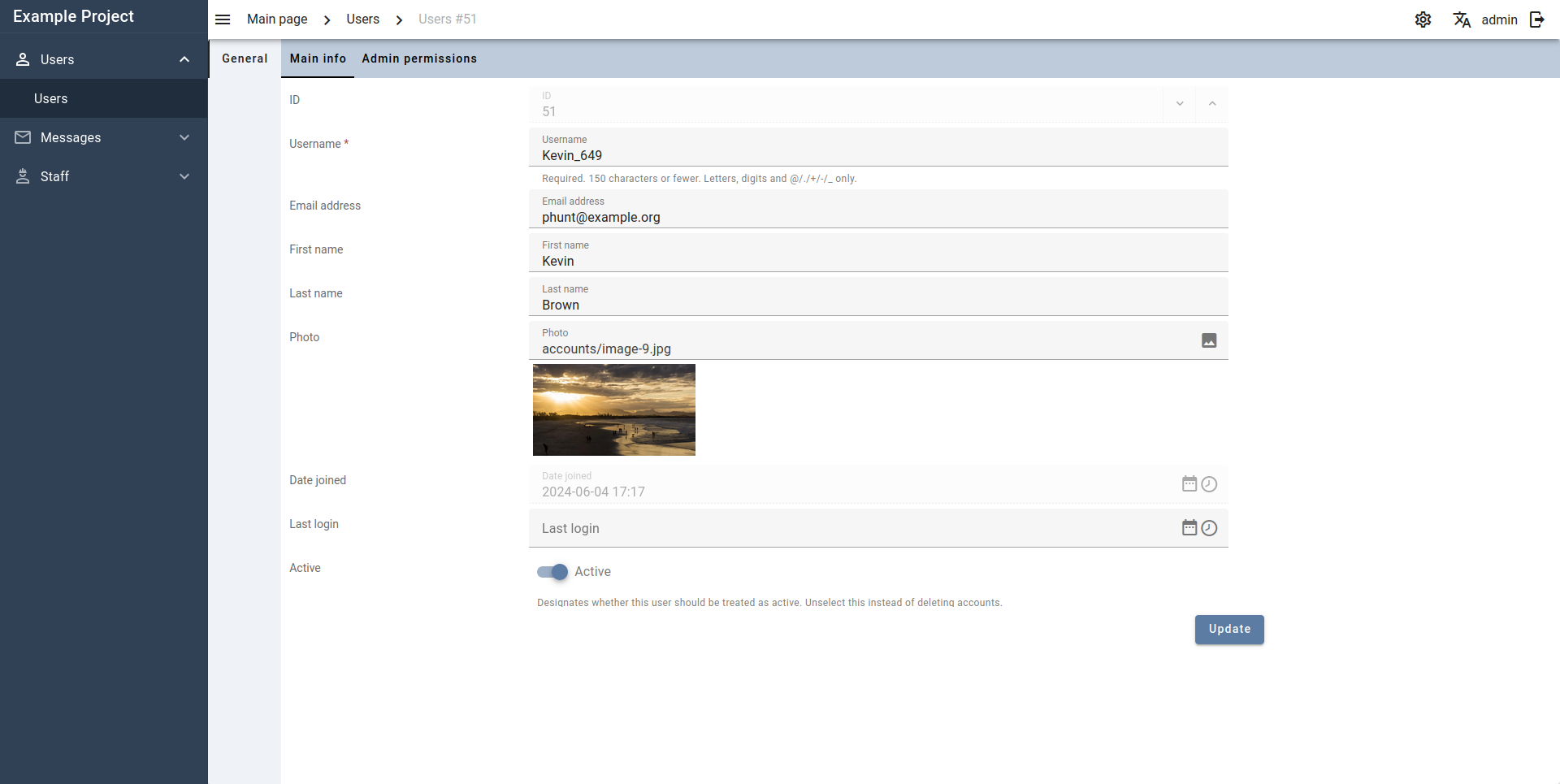
Table page
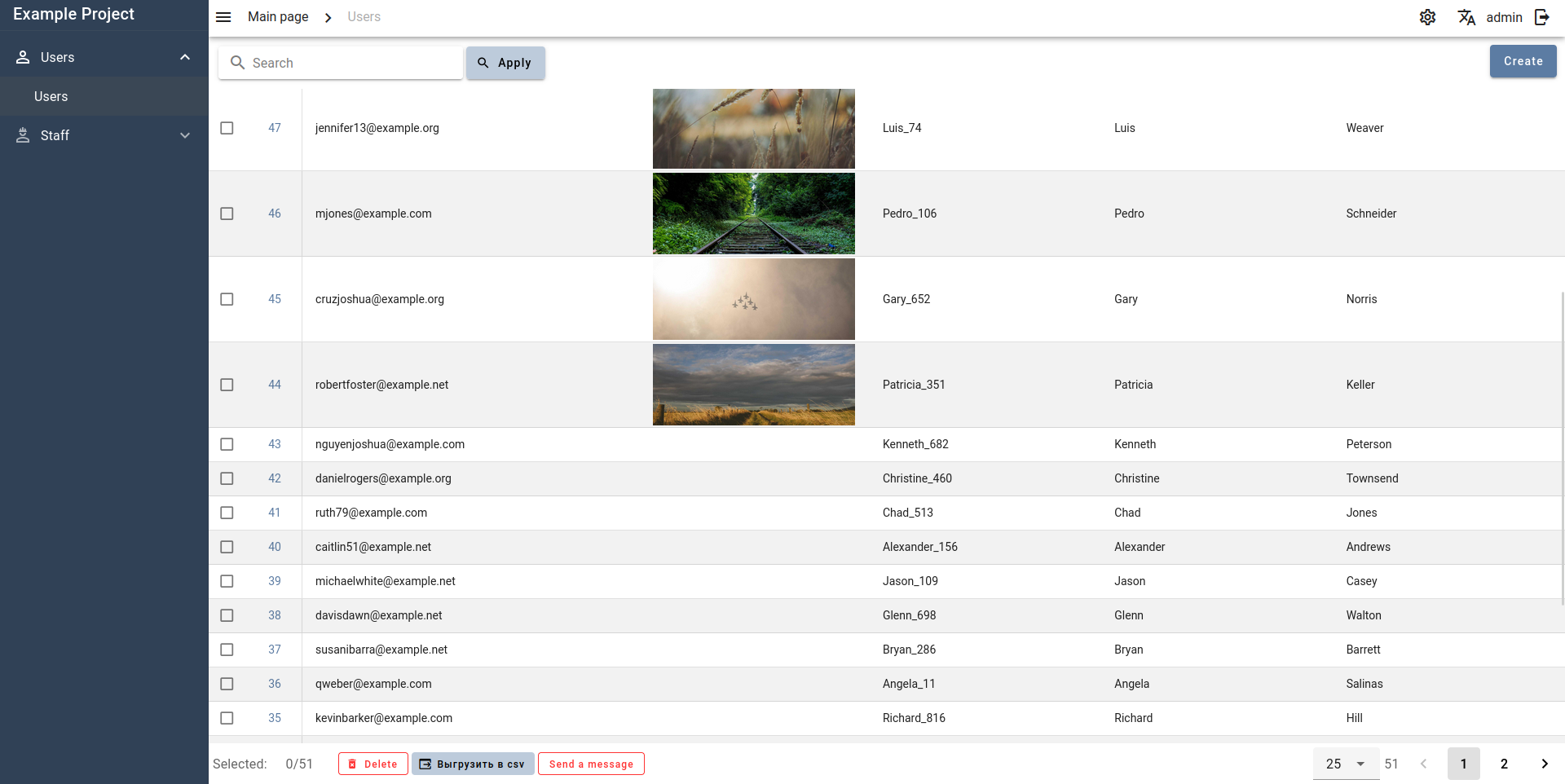
Color schemes
Installation
Dependencies
Django==4.2.7
django-filter==23.3
djangorestframework==3.14.0
Optional:
django-import-export==4.1.0- for import/exportdjango-modeltranslation==0.18.11- for translationsdjango-ordered-model==3.7.4- for ordered models
DCA installation:
pip install django-customvueadmin
Django settings:
INSTALLED_APPS
settings.py
INSTALLED_APPS = [
...
'rest_framework.authtoken',
'custom_admin',
]
REST_FRAMEWORK = {
'DEFAULT_AUTHENTICATION_CLASSES': [
'rest_framework.authentication.TokenAuthentication',
]
}
Adding urls:
from django.urls import include, path, re_path
from custom_admin.views import CustomAdminView
urlpatterns = [
re_path(r'^admin/.*$', CustomAdminView.as_view()),
path('custom_admin/', include('custom_admin.api.urls')),
]
Make sure the static files are available:
from django.conf import settings
from django.conf.urls.static import static
from django.contrib.staticfiles.urls import staticfiles_urlpatterns
urlpatterns += staticfiles_urlpatterns() + static(
settings.MEDIA_URL, document_root=settings.MEDIA_ROOT
)
Settings:
The ability to customize the admin panel is provided via CUSTOM_ADMIN:
CUSTOM_ADMIN = {
'title': env.str('CUSTOM_ADMIN_TITLE', SITE_TITLE),
}
Available settings:
-
title
Admin tab header title.
Used to call an api from the interface side. -
admin_prefix
Path where admin page will be accessable, whereCustomAdminViewis located.
Default:/admin/ -
backend_prefix
The endpoint by which the admin API will be accessed from front-end, wherecustom_admin.api.urlsis located.
Default:/custom_admin/
If you have not specified this setting explicitly with domain and you are using https, you need this setting:
# Setting in case of https:
USE_X_FORWARDED_HOST = True
SECURE_PROXY_SSL_HEADER = ('HTTP_X_FORWARDED_PROTO', 'https')
-
logo_image
Path for the admin logo.
Default:None -
favicon_image
Path for the favicon image.
Default:/static/custom_admin/favicon.ico
Languages
The LANGUAGES default setting is used to configure the languages that will be available for selection.
LANGUAGES = [
('ru', 'Russian'),
('en', 'English'),
]
Phrases available for translation
from django.utils.translation import gettext_lazy as _
_('Create')
_('Edit')
_('Action')
_('Admin')
_('Section')
_('Title')
_('Action type')
_('Log content')
_('Admin action log')
_('Admin action logs')
_('Delete')
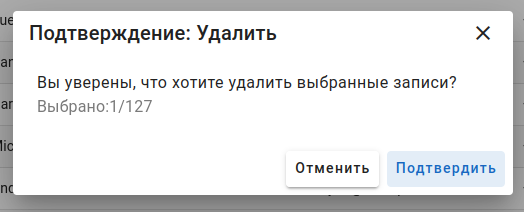
_('Are you sure you want to delete the selected records?')
_('The records have been successfully deleted!')
_('It is not possible to delete some model instances because they are referenced via protected foreign keys: %(objects)s')
_('Records have been successfully deleted!')
_('The option ‘%(title)s’ is not among the available options.')
# Permissions:
_('View')
_('Create')
_('Change')
_('Destroy')
_('Send action')
Adding sections and pages
In settings.py you need to add a parameter ADMIN_URLS.
View-set's are added dynamically to avoid cyclic dependencies.
import typing
from django.utils.translation import gettext_lazy as _
from custom_admin.api.viewset_info import AdminViewSetInfo
ADMIN_URLS: typing.List[AdminViewSetInfo] = [
AdminViewSetInfo(
group_slug='users',
title=_('users'),
icon='el-icon-user',
views=[
'apps.users.custom_admin.UserAdminViewSet',
]
),
AdminViewSetInfo(
group_slug='staff',
title=_('staff'),
icon='el-icon-service',
views=[
'custom_admin.api.views.defaults.AdminLogAdminViewSet',
'custom_admin.api.views.defaults.GroupAdminViewSet',
'custom_admin.api.views.defaults.PermissionsAdminViewSet',
]
),
]
Viewsets
Module containing viewset classes: custom_admin.api.views
Example:
from custom_admin.api.views.base_admin_viewset import BaseAdminViewSet
from django.contrib.auth.models import Group
from django.utils.translation import gettext_lazy as _
class GroupAdminViewSet(BaseAdminViewSet):
title = _('Roles')
queryset = Group.objects.all()
search_fields = ('name', )
list_display = (
'id',
'name',
)
Available types:
Viewsets must be inherited from the following classes:
-
BaseAdminViewSet
Base admin viewset class. -
ReadOnlyBaseAdminViewSet
Read only viewset. -
WithoutCreateBaseAdminViewSet
Viewset without create option but can be updated. -
WithoutUpdateBaseAdminViewSet
Viewset without update option. -
ListBaseAdminViewSet
Only list view (without detail) -
BaseAdminDataViewSet
Non ORM data oriented viewset
Serializers
In case serializer_class is not specified - will be used default one with fields = '__all__' Meta option
Serializer fixed columns
Viewset parameter fixed_columns allows to specify fields that will be fixed when horizontal scrolling.
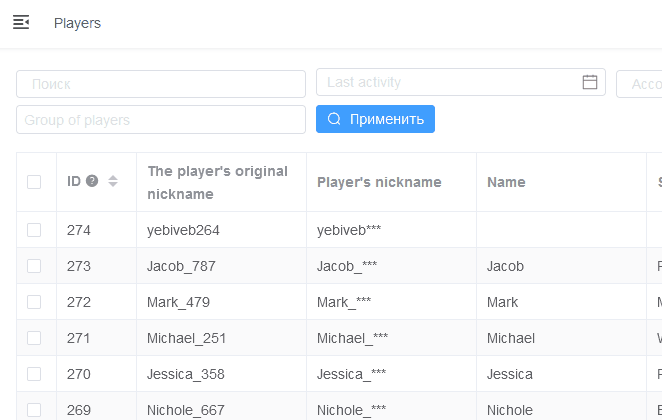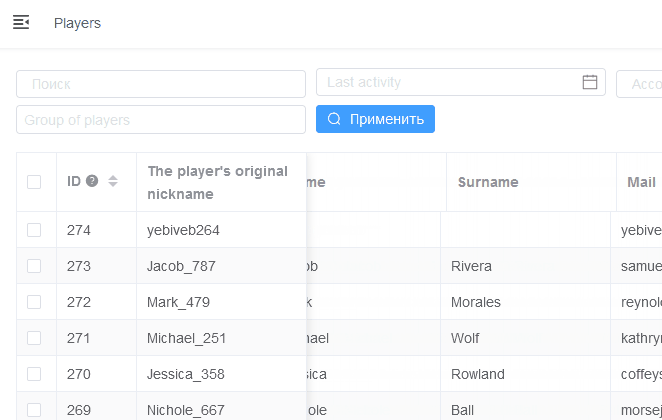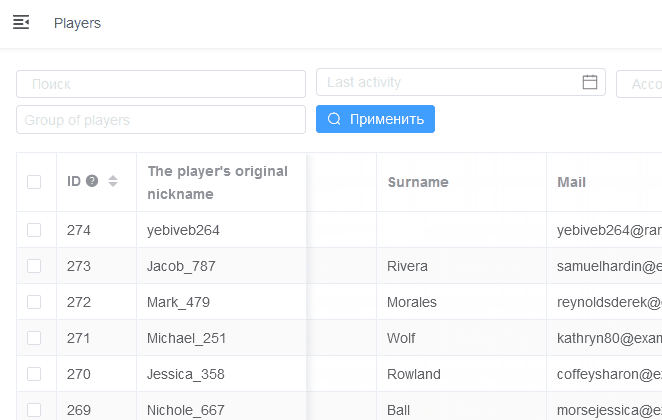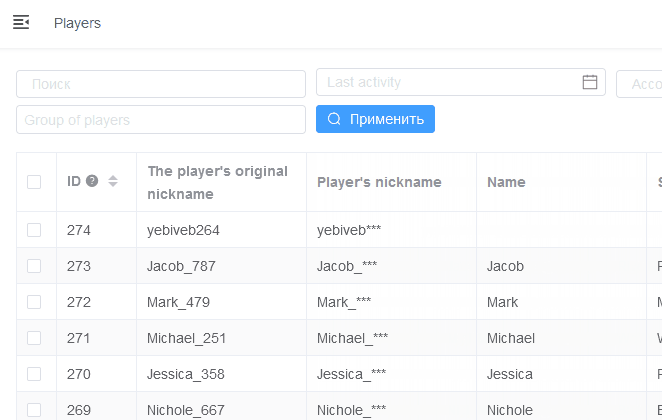
Example
fixed_columns = (
'id',
'username',
)
Models settings
Autocomplete search
Model attribute admin_autocomplite_fields is specify which fields will be used for autocomplete search (filters, related fields).
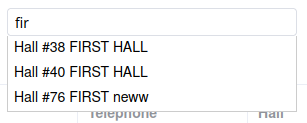
admin_autocomplite_fields = ('id', 'nickname')
Filter for autocomplete
Classmethod autocomplete_filter allowes to controll results from autocomplete:
@classmethod
def autocomplete_filter(cls, request, qs, info):
if info.action_name == 'send_message_action':
qs = qs.filter(is_marketing_mailing=True)
return qs
info is instance of custom_admin.api.views.autocomplete.AutocompleteInfo
Actions
In viewset actions list, you can specify functions that can be called from the list view.
You can specify settings through decorator custom_admin.api.admin_action
Available settings:
-
short_description
The name that will be displayed as title. -
form_serializer
Optional parameter for action form output. -
description
The text that will be displayed next to the title on the popup form.
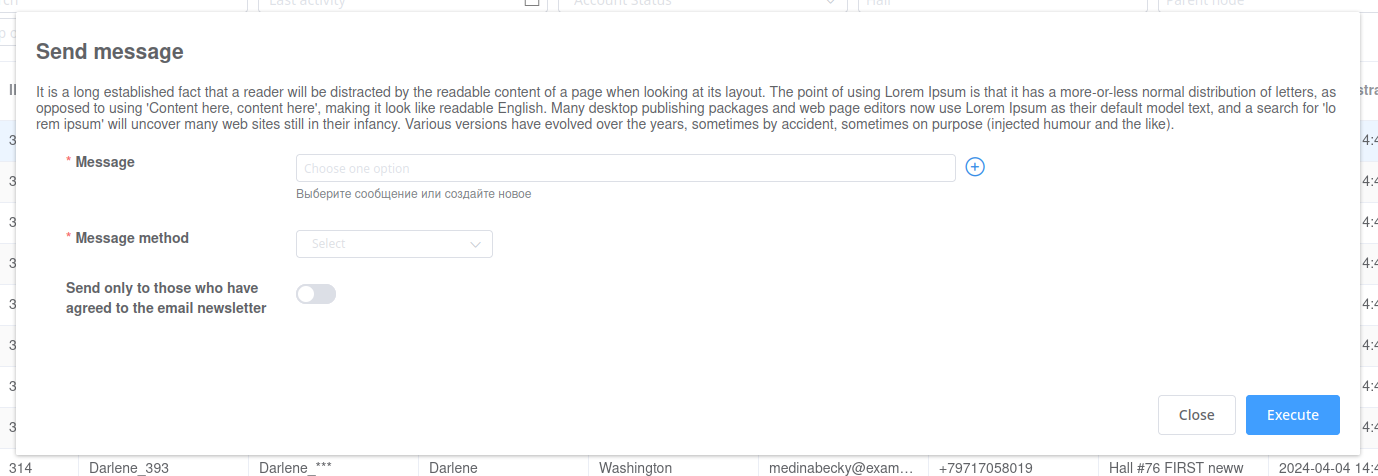
confirmation_text
Text output to confirm that the action has been performed.
-
base_color
Any rgb or html colors. -
variant
Options: elevated, flat, tonal, outlined, text, and plain.
Response messages format
custom_admin.api.actions.action_result.ActionResult is used for message output.
return ActionResult(messages=[_('Success')])
- List messages with status code:
return ActionResult(messages=[_('Error')], status_code=400)
ResponseorHttpResponseinstance for custom responses:
response = HttpResponse(f, content_type='text/csv')
response['Pragma'] = filename
response['Content-Disposition'] = f'attachment; filename="{filename}"'
f.close()
return response
Persistent message
Ability to display a message to the administrator that will not be hidden automatically. html tags allowed.
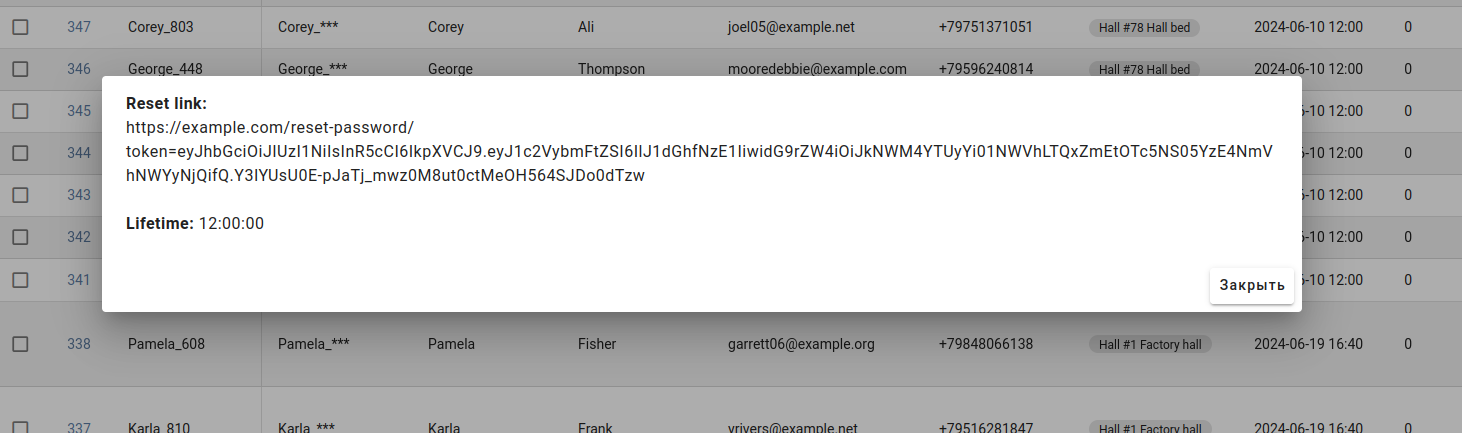
from custom_admin.api import admin_action
from custom_admin.api.actions.action_result import ActionResult
from django.utils.translation import gettext as _
MESSAGE = '''
<b>Reset link:</b><br>
{url}<br>
<br>
<b>Lifetime:</b> {livetime}
'''
@admin_action(
short_description=_('Получить ссылку на сброс пароля'),
icon='mdi-lock-outline',
)
def reset_password_link(view, request, queryset, *args, **kwargs) -> ActionResult:
...
msg = MESSAGE.format(
url=url,
livetime=datetime.timedelta(seconds=lifetime),
)
return ActionResult(persistent_message=msg)
Action form
In form_serializer parameter you can pass instance of AdminSerializer to display the form before submitting the action.

from custom_admin.api import fields
from custom_admin.api.serializers import AdminSerializer
class AdminSendMessageSerializer(AdminSerializer):
message = fields.AdminPrimaryKeyRelatedField(
queryset=Message.objects.all(),
label=_('Message'),
required=True,
)
send_method = fields.AdminChoiceField(
label=_('Method'),
choices=MessageType.choices,
required=True
)
class Meta:
fields = [
'message', 'send_method',
]
from custom_admin.api import admin_action
@admin_action(
short_description=_('Send a message'),
form_serializer=AdminSendMessageSerializer,
base_color='#ff3333',
variant='outlined',
)
def send_message_action(view, request, queryset, form_data):
serializer = AdminSendMessageSerializer(data=form_data)
serializer.is_valid(raise_exception=True)
message = serializer.validated_data['message']
...
return 'Success', 200
actions = BaseAdminViewSet.actions + [
send_message_action,
]
Django import / export support
To use import/export in viewset, resource must be specified.
class UserResource(resources.ModelResource):
tags = ifields.Field(attribute='tags', widget=ManyToManyWidget(Tag, field='name', separator=','))
class Meta:
model = User
from custom_admin.api import actions
class UsersAdminViewSet(BaseAdminViewSet):
resource = UserResource
actions = [actions.admin_export, actions.admin_import]
Serizlisers
AdminModelSerializer
Viewset serializers must be inherited from custom_admin.api.serializers.AdminModelSerializer class.
AdminModelSerializer provided:
- Custom fields
- Functionality for logging actions inside the admin panel
TranslatedModelSerializer

Requires library django-modeltranslation
Provides the ability to automatically add fields with translations to the serializers.
OrderedAdminModelSerializer
Requires library django-ordered-model
Calls OrderedModel.to() method to effect a re-ordering.
order_field can be specified or model.order_field_name will be used.
Serializers fields
AdminPrimaryKeyRelatedField
Available options:
-
update_only- boolean -
create_only- boolean -
filter_queryset- functionfilter_currency_info(qs, form_data: dict, request=None)
It allows to provide results for selection depending on other form fields.
form_data - contains dict with form data containing all fields.
qs - initial queryset.
Example:
from custom_admin.api.serializers import AdminModelSerializer
from custom_admin.api.views.base_admin_viewset import BaseAdminViewSet
from django.utils.translation import gettext_lazy as _
from apps.users.models import User
class UserAdminSerializer(AdminModelSerializer):
class Meta:
fields = (
'id',
'username',
'email',
'first_name',
'last_name',
'photo',
'date_joined',
'last_login',
'is_active',
'is_superuser',
'is_staff',
'groups',
'user_permissions',
)
groups = [
{'title': _('Main info'), 'fields': (
'id',
'username',
'email',
'first_name',
'last_name',
'photo',
'date_joined',
'last_login',
'is_active',
)},
{'title': _('Admin permissions'), 'fields': (
'is_superuser',
'is_staff',
'groups',
'user_permissions',
)},
]
model = User
extra_kwargs = {
'photo': {'list_preview': True},
'date_joined': {'read_only': True},
}
class UsersAdminViewSet(BaseAdminViewSet):
serializer_class = UserAdminSerializer
queryset = User.objects.all()
search_fields = (
'username',
'email',
'first_name',
'last_name',
)
list_display = (
'id',
'email',
'photo',
'username',
'first_name',
'last_name',
)
Serializer field groups
You can specify the groups parameter inside serializer Meta class to have your fields displayed in different sections.
This is purely for visual display on the front. The update request will work as before.
Each groups element must contain:
-
title
String name for display inside sections (tabs). -
fields
List of serializer fields.
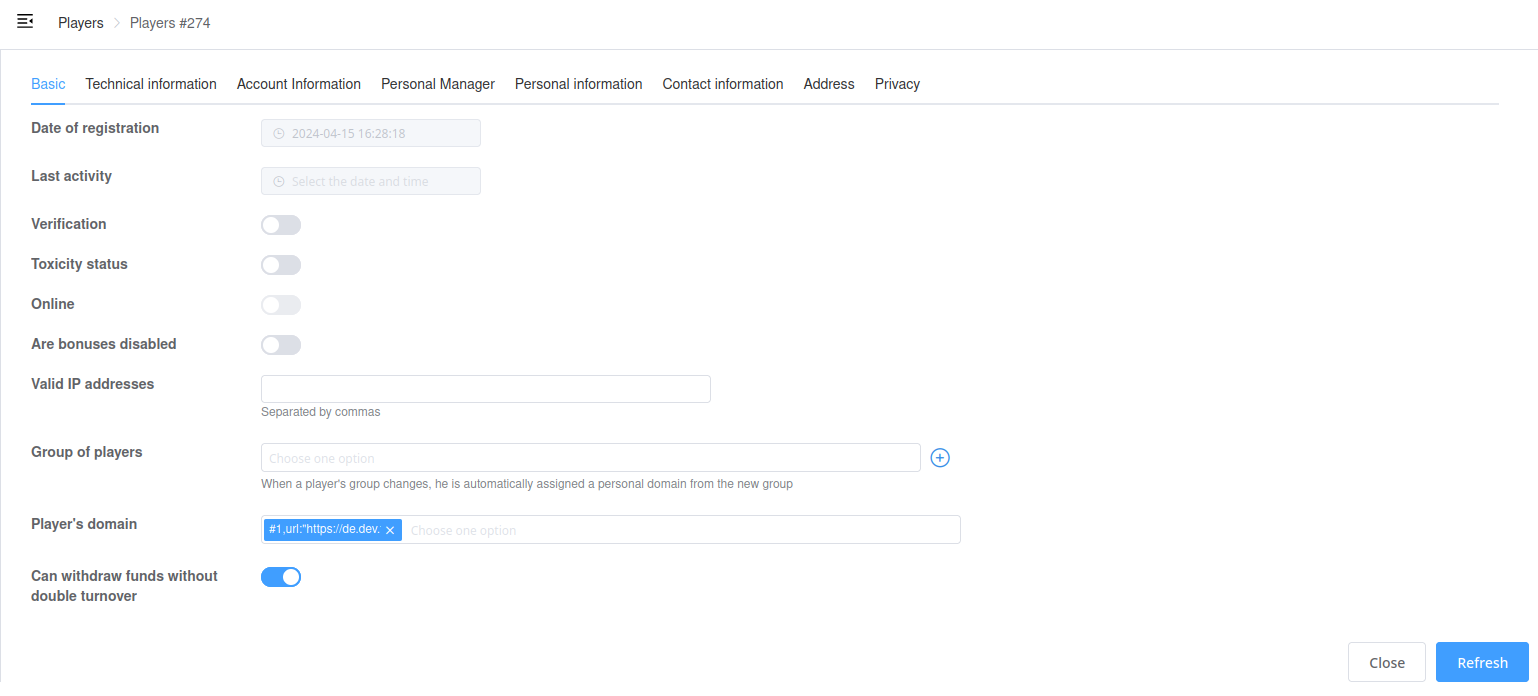
Example
class Meta:
model = User
groups = [
{'title': _('Base info'), 'fields': (
'verification',
'allowed_ip',
'date_joined',
'last_activity',
'is_online',
'group',
)},
{'title': _('Tech info'), 'fields': (
'external_id',
'last_visit_datetime',
'last_visit_language',
'last_visit_device',
'last_visit_ip',
'last_visit_geo_ip',
)},
]
Serializer field options
Tag style
tag_style - option to specify a color for certain string values
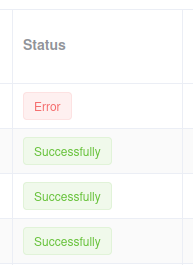
Example
Serializer:
class Meta:
model = Payment
extra_kwargs = {
'status': {'tag_style': TransactionStatus.get_style()},
}
Styles:
@classmethod
def get_style(cls):
return {
cls.SUCCESS.value: 'green',
cls.ERROR.value: 'red',
}
Wysiwyg
wysiwyg - option to enable TinyMCE editor.
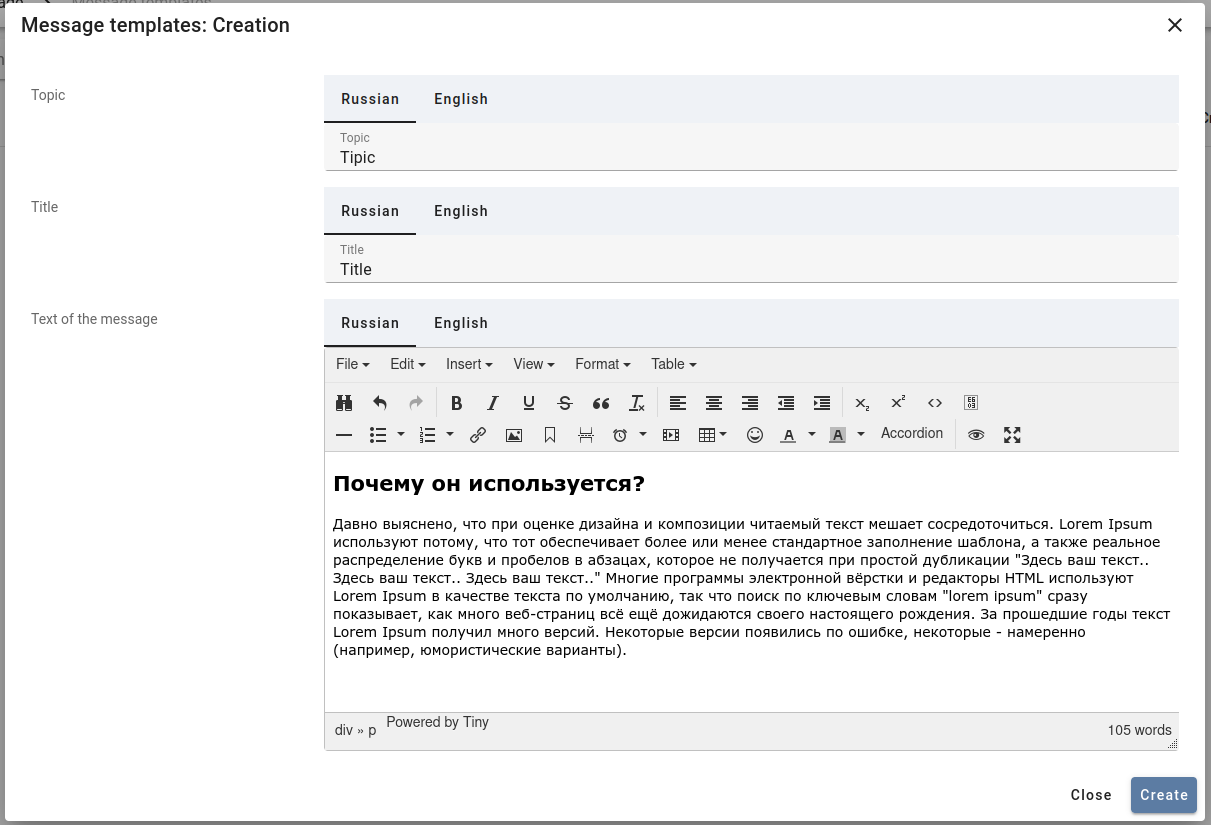
Example
extra_kwargs = {
'description': {'wysiwyg': True},
}
Multiline
multilined - option to specify a text field in multiple lines.
Example
extra_kwargs = {
'note': {'multilined': True},
}
Table image preview
list_preview - display image inside table list.
Example
extra_kwargs = {
'image': {'list_preview': True},
}
JSON Forms
It is possible to create custom forms for JSON fields on the project, JSONForms lib is used for this purpose.
To use this field, you need to add the json_forms with schema and uischema parameter to the field in the serializer.
Example:
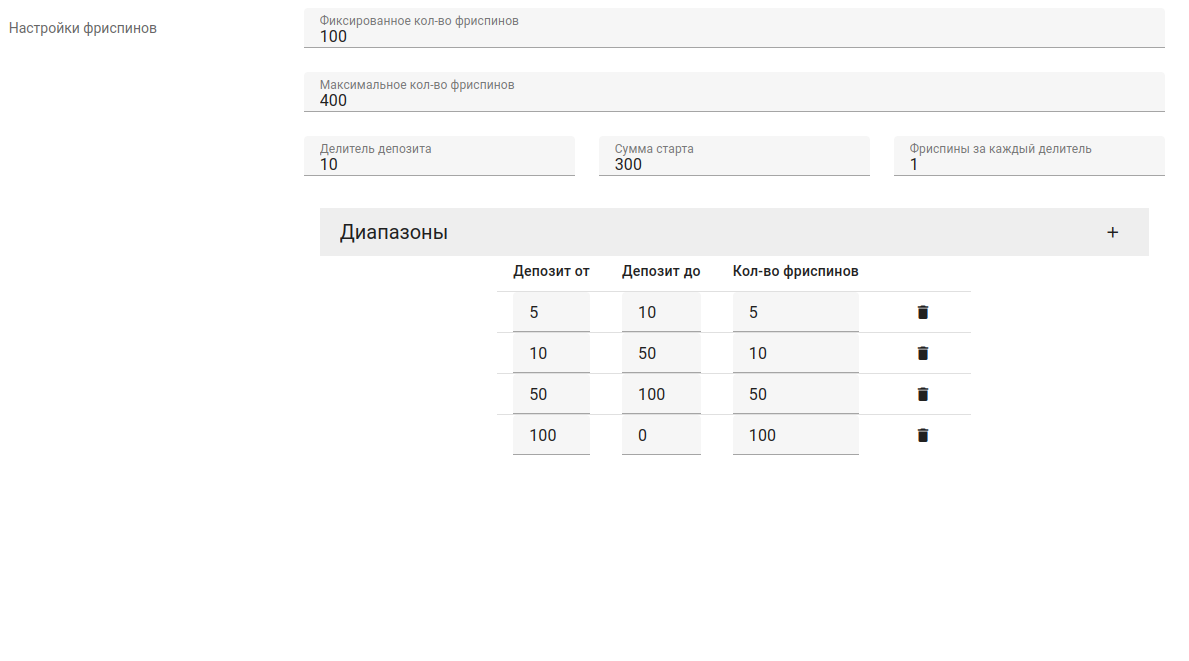
JSON_FORMS = {
'schema': {
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"max_total": {
"title": _("Максимальное кол-во фриспинов"),
"type": "number",
},
"fix_value": {
"title": _("Фиксированное кол-во фриспинов"),
"type": "number",
},
"division": {
"title": _("Делитель депозита"),
"type": "number",
},
"division_from": {
"title": _("Сумма старта"),
"type": "number",
},
"division_value": {
"title": _("Фриспины за каждый делитель"),
"type": "number",
},
"ranges": {
"type": "array",
"items": {
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"from": {
"title": _("Депозит от"),
"type": "number",
},
"to": {
"title": _("Депозит до"),
"type": "number",
},
"value": {
"title": _("Кол-во фриспинов"),
"type": "number",
}
}
}
}
}
},
'uischema': {
"type": "VerticalLayout",
"elements": [
{
"type": "Control",
"scope": "#/properties/fix_value"
},
{
"type": "Control",
"scope": "#/properties/max_total"
},
{
"type": "Category",
"elements": [
{
"type": "HorizontalLayout",
"elements": [
{
"type": "Control",
"scope": "#/properties/division"
},
{
"type": "Control",
"scope": "#/properties/division_from"
},
{
"type": "Control",
"scope": "#/properties/division_value"
},
],
},
],
},
{
"type": "Control",
"label": _("Диапазоны"),
"scope": "#/properties/ranges",
},
]
}
}
class Meta:
...
extra_kwargs = {
json_field': {'json_forms': FREESPINS_JSON_FORMS},
}
Viewset Related inlines
The related_inlines parameter allows you to add related lnlines viewsets settings. It is possible to add both ORM and non-ORM viewsets.
Each setting must be an instance of RelatedInline.
Attributes of RelatedInline
-
title
Displayed title in sections (tabs) -
viewset_name
Name of viewset.
You can use the django manage command to show all sets of admin views:
manage.py custom_admin_viewsets_list
-
inline_slug
The unique string that will be used in the url. -
icon
Icon. List list -
back_relation_name
Optional. It's necessary for ORM relations. You need to specify a field or lookup for the reverse filter.
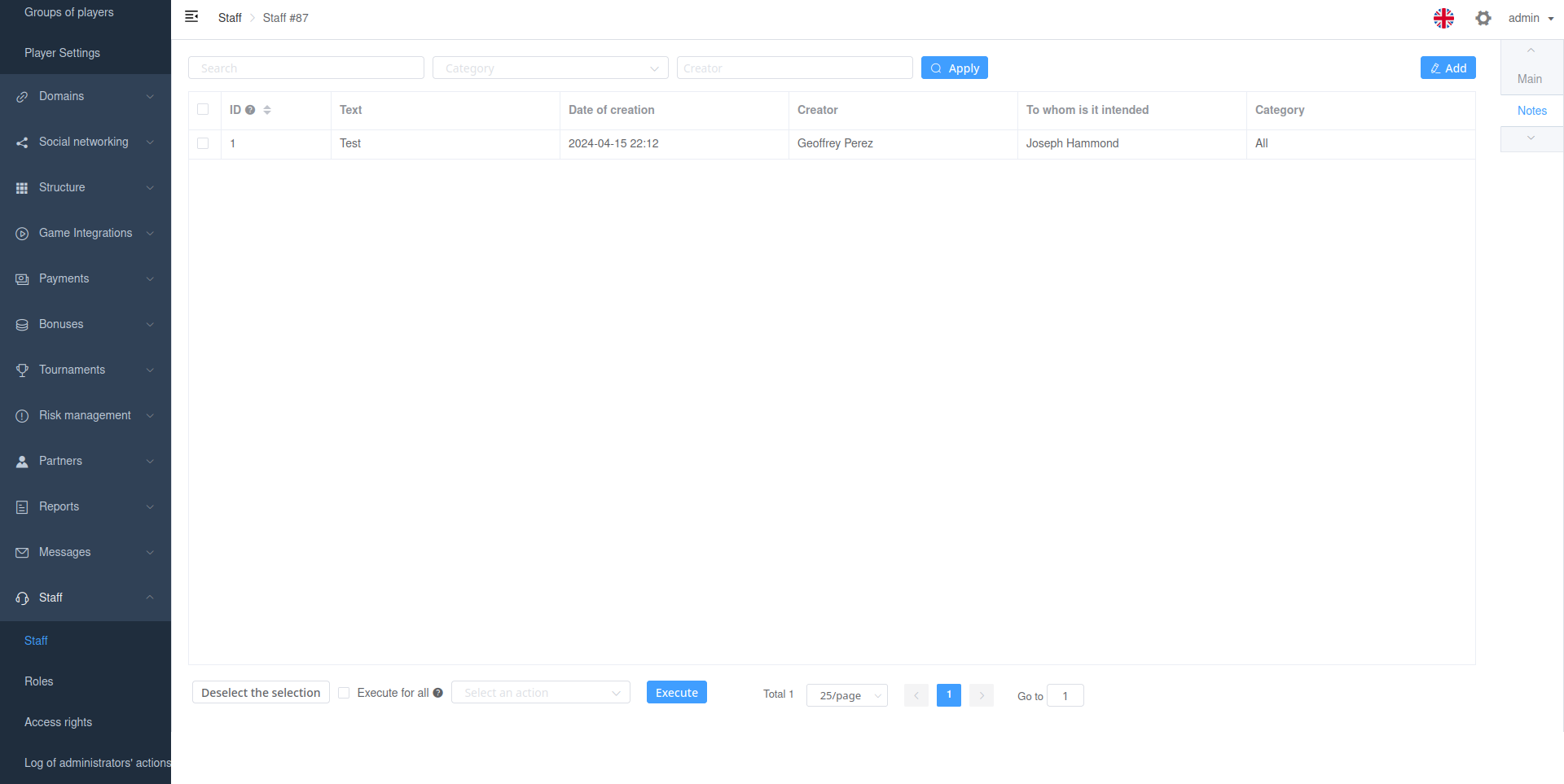
ORM inline
For ORM inline you just need specify back_relation_name.
For non-ORM inlines, check out the section Non ORM Inlines.
Example
import typing
from custom_admin.api import RelatedInline
class StaffAdminViewSet(BaseAdminViewSet):
...
related_inlines: typing.List[RelatedInline] = [
RelatedInline(
viewset_name='note',
back_relation_name='user',
inline_slug='staff_notes',
title=_('Notes'),
),
]
Filters
Class BaseAdminFilterSet allows to create filters without models.
from custom_admin.api.filters import BaseAdminFilterSet
from django_filters import rest_framework as filters
class FinancesFilterSet(BaseAdminFilterSet):
date = filters.DateFromToRangeFilter(label=_('Time range'))
currencies = fields.AdminPrimaryKeyRelatedField(
label=_('Currency'),
queryset=Currency.objects.order_by('-priority'),
many=True,
required=False,
)
Table
Viewset action with inline_type InlinesType.TABLE.
Must return InlineTableResult instance.
You can use django.core.paginator.Paginator for paginated response.
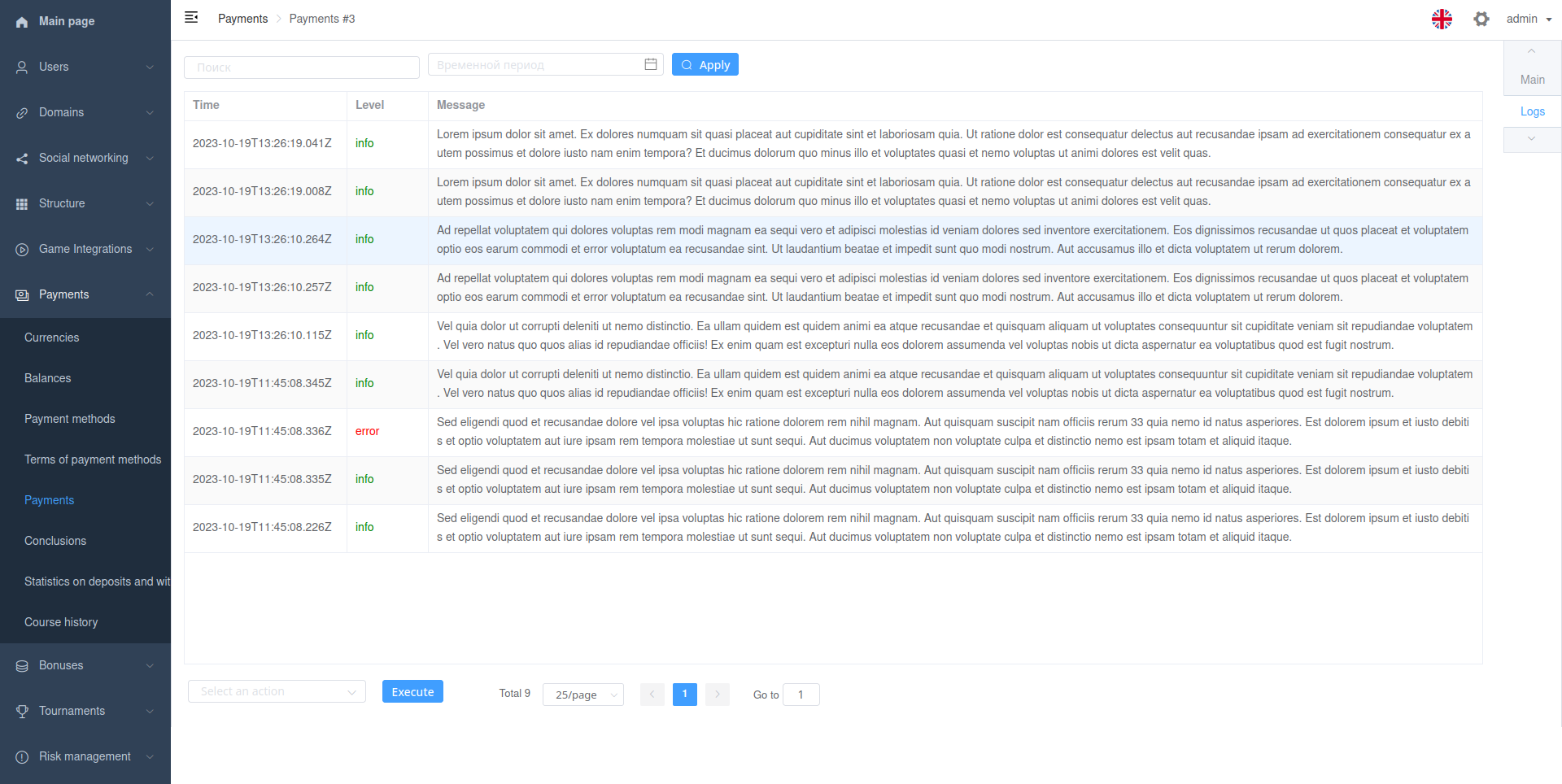
Example
from django_filters import rest_framework as filters
class LogsFilterSet(BaseAdminFilterSet):
search_text = filters.CharFilter(label=_('Search'))
date = filters.DateFromToRangeFilter(label=_('Time range'))
from django.core.paginator import Paginator
...
@action(
name=_('Logs'),
methods=['post'],
detail=True,
permission_classes=[AdminPermission, ],
inline_type=InlinesType.TABLE,
actions=[export_csv_inline],
filterset_class=LogsFilterSet,
)
def logs(self, request, pk, filters, *args, **kwargs):
page = request.GET.get('page', 1)
page_size = request.GET.get('limit', settings.REST_FRAMEWORK['PAGE_SIZE'])
search_text = filters.get('search_text', None)
log_result = ...
data = [[log.asctime, log.level_colored, log.msg] for log in log_result.logs]
paginator = Paginator(data, page_size)
return InlineTableResult(
messages=messages,
columns=['Time', 'Level', 'Message'],
data=paginator.page(page),
paginator=paginator,
columns_info={
'Time': ColumnInfo(width=200),
'Level': ColumnInfo(width=100, html=True),
}
)
Graph
Viewset action with inline_type InlinesType.GRAPH.
Must return InlineGraphResult instance. Can contain many charts with ChartData.
Uses chartjs library to output graphs.
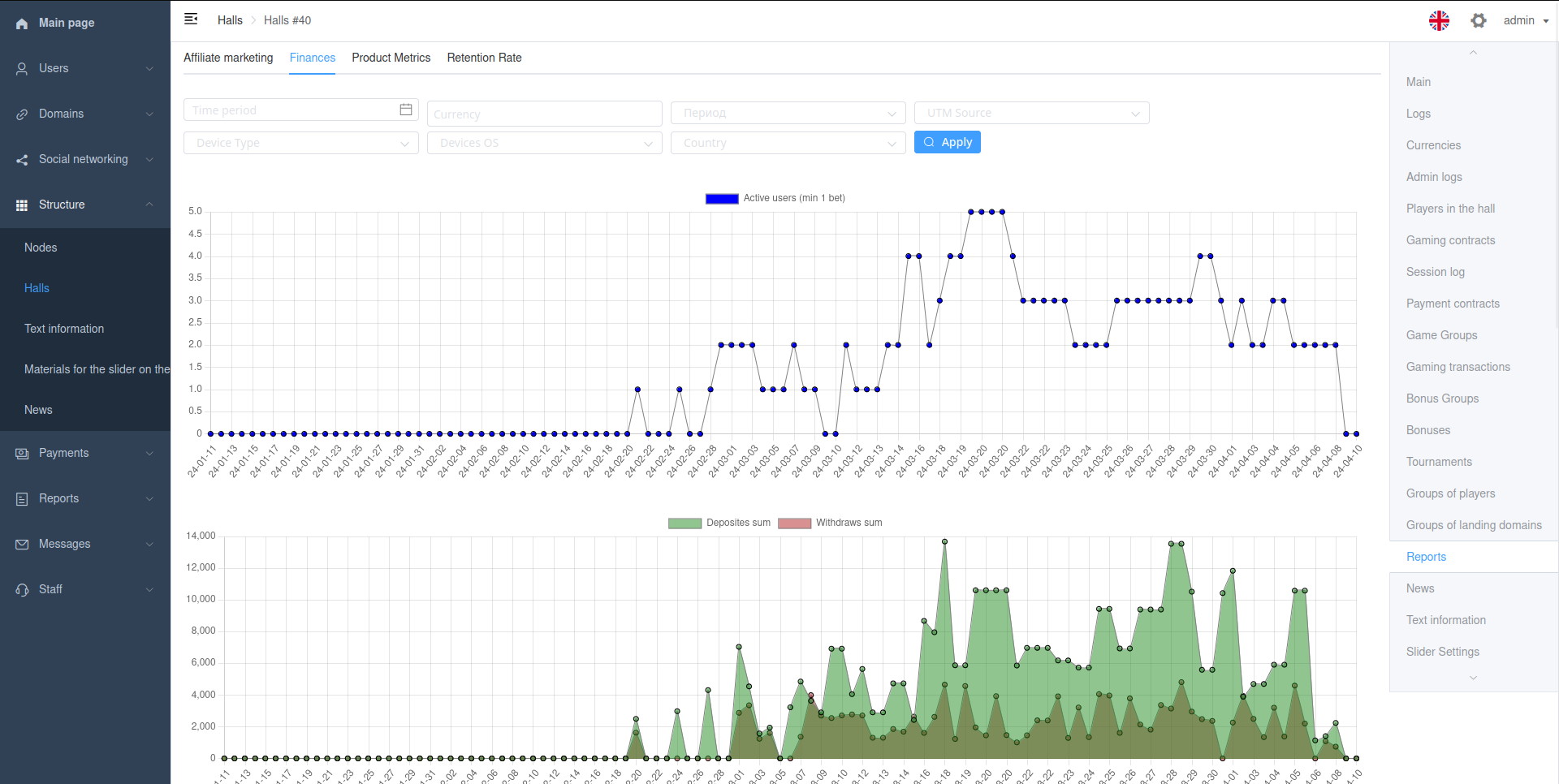
Example
@action(
name='Finances',
filterset_class=FinancesFilterSet,
methods=['post'],
detail=True,
permission_classes=[IsStaffPermission, ],
inline_type=InlinesType.GRAPH,
)
def finances(self, request, pk, filters, *args, **kwargs):
...
labels = [r['time'].strftime('%y-%m-%d') for r in result]
graph = InlineGraphResult(
charts=[
ChartData(
labels=labels,
datasets=[
GraphDataset(
label='Active users',
data=[r['Active users'] for r in result],
backgroundColor='Blue',
),
],
),
ChartData(
labels=labels,
datasets=[
GraphDataset(
label='Deposites sum',
data=[r['Deposites sum'] for r in result],
backgroundColor='rgba(34, 139, 34, 0.5)',
fill='origin',
),
GraphDataset(
label='Withdraws sum',
data=[r['Withdraws sum'] for r in result],
backgroundColor='rgba(178, 34, 34, 0.5)',
fill='origin',
),
],
),
],
)
return graph
Permissions
Permissions that are used to access the admin panel may be different from the standard django ones.
Manage command to sync permissions:
manage.py sync_permissions
